Updated February 16, 2020
Background
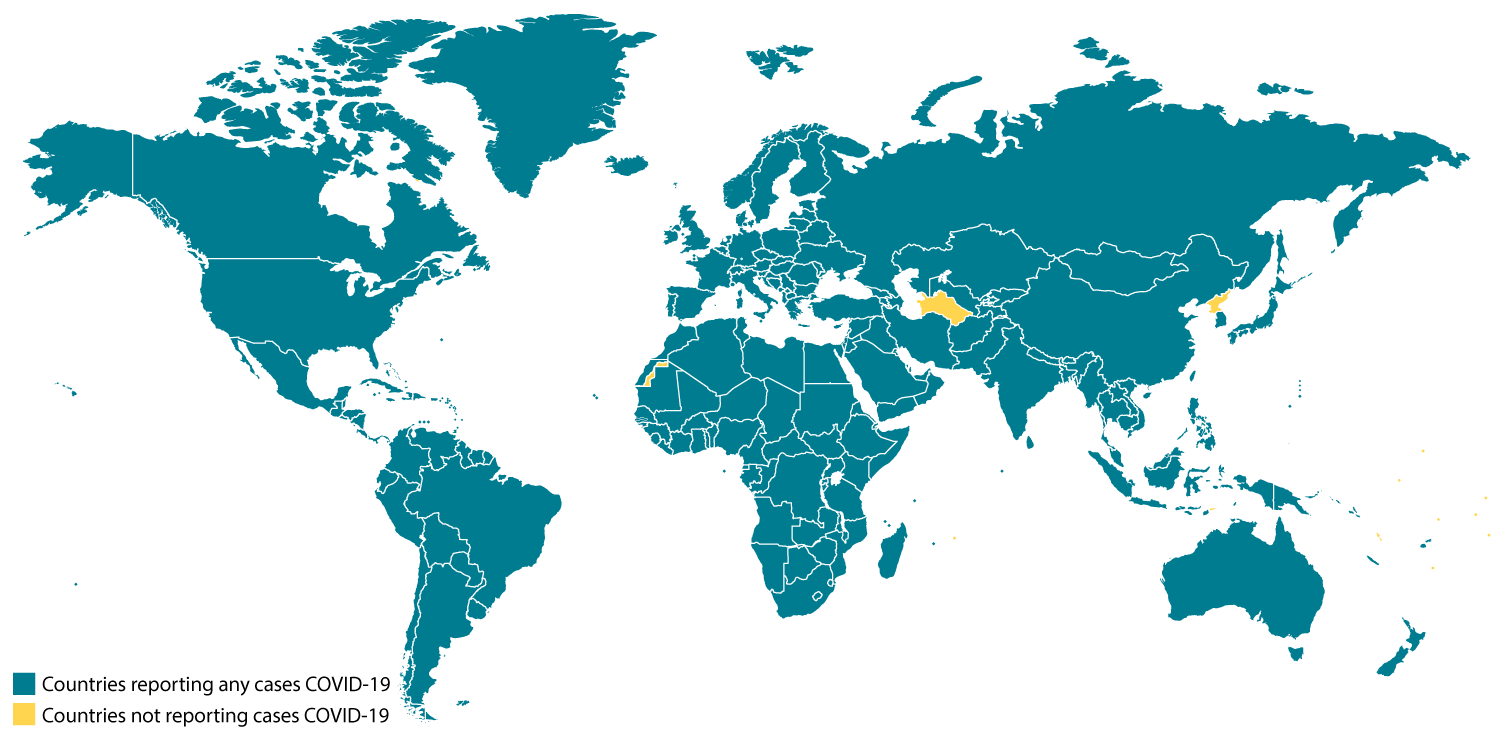
CDC is closely monitoring an outbreak of respiratory disease caused by a novel (new) coronavirus that was first detected in Wuhan City, Hubei Province, China and which continues to expand. On February 11, 2020, the World Health Organization named the disease coronavirus disease 2019 (abbreviated “COVID-19”).
Chinese health officials have reported tens of thousands of cases of COVID-19 in China, with the virus reportedly spreading from person-to-person in parts of that country. COVID-19 illnesses, most of them associated with travel from Wuhan, also are being reported in a growing number of international locations, including the United States. Some person-to-person spread of this virus outside China has been detected. The United States reported the first confirmed instance of person-to-person spread with this virus on January 30, 2020.
On January 30, 2020, the International Health Regulations Emergency Committee of the World Health Organization declared the outbreak a “public health emergency of international concernexternal icon” (PHEIC). On January 31, 2020, Health and Human Services Secretary Alex M. Azar II declared a public health emergency (PHE) for the United States to aid the nation’s healthcare community in responding to COVID-19. Also on January 31, the President of the United States signed a presidential “Proclamation on Suspension of Entry as Immigrants and Nonimmigrants of Persons who Pose a Risk of Transmitting 2019 Novel Coronavirusexternal icon.” These measures were announced at a press briefing by members of the President’s Coronavirus Task Forceexternal icon.
Coronaviruses are a large family of viruses that are common in many different species of animals, including camels, cattle, cats, and bats. Rarely, animal coronaviruses can infect people and then spread between people such as with MERS-CoV, SARS-CoV, and now with this new virus (named SARS-CoV-2).
Source and Spread of the Virus
Chinese health officials have reported tens of thousands of cases of COVID-19 in China, with the virus reportedly spreading from person to person in parts of that country. COVID-19 illnesses, most of them associated with travel from Wuhan, also are being reported in a growing number of international locations, including the United States. Some person-to-person spread of this virus outside China has been detected. The United States reported the first confirmed instance of person-to-person spread with this virus on January 30, 2020.
The SARS-CoV-2 virus is a betacoronavirus, like MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV, both of which have their origins in bats. The sequences from U.S. patients are similar to the one that China initially posted, suggesting a likely single, recent emergence of this virus from an animal reservoir.
Early on, many of the patients in the COVID-19 outbreak in Wuhan, China had some link to a large seafood and live animal market, suggesting animal-to-person spread. Later, a growing number of patients reportedly did not have exposure to animal markets, indicating person-to-person spread. Chinese officials report that sustained person-to-person spread in the community is occurring in China. Person-to-person spread has been reported outside China, including in the United States and other countries. Learn what is known about the spread of newly emerged coronaviruses.